2. GOP Structure and Applicable Scenarios¶
2.1. GOP Mode List¶
Mode |
Description |
|---|---|
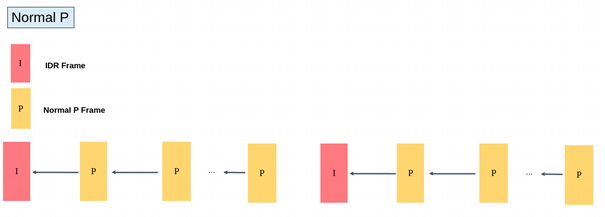
NormalP |
The P frame only refers to the previous reference frame |
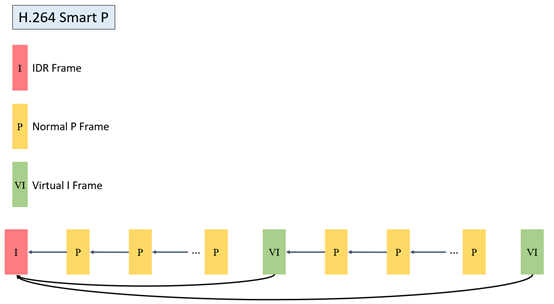
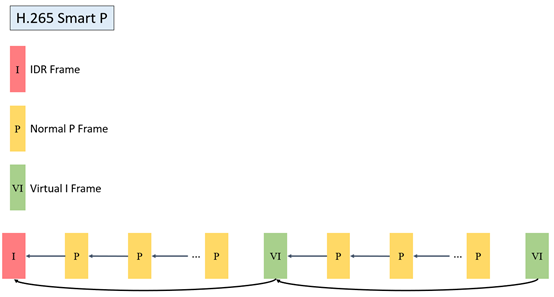
SmartP |
The P frame only refers to the previous reference frame, and the VI frame refers to the previous IDR frame |
2.2. Description and Usage of NormalP mode GOP structure¶
2.2.1. Description of NormalP mode GOP structure¶
2.2.2. Usage of NormalP mode GOP structure¶
Related interface
CVI_MPI_VENC_CreateChn
Related parameters
VENC_CHN_ATTR_S::stGopAttr.enGopMode = VENC_GOPMODE_NORMALP
VENC_CHN_ATTR_S::stRcAttr.u32Gop = 60;
VENC_CHN_ATTR_S::stGopAttr.stNormalP.s32IPQpDelta is recommended to set to 3.
The larger the value, the higher the bitrate of the I-frame and the better the image quality.
2.3. Description and Usage of SmartP mode GOP structure¶
2.3.1. Description of SmartP mode GOP structure¶
2.3.2. Usage of SmartP mode GOP structure¶
Related interface
CVI_VENC_CreateChn
Related parameters
VENC_CHN_ATTR_S::stGopAttr.enGopMode = VENC_GOPMODE_SMARTP
VENC_CHN_ATTR_S::stGopAttr.stSmartP.u32BgInterval = 300; // 10secs for fps=30
VENC_CHN_ATTR_S::stRcAttr.u32Gop = 60; // virtual I interval, 2 secs for fps=30
VENC_CHN_ATTR_S::stRcAttr.u32StatTime = 10 // secs
VENC_CHN_ATTR_S:: stGopAttr.stSmartP.s32BgQpDelta = 4
2.4. Memory usage, latency, application scenarios and compatibility of GOP Structure¶
Mode |
DDR usage |
Latency |
Applicable Scenarios |
H.264 / H.265 Enc |
H.264 / H.265 Enc |
||
NormalP |
2*PicSize |
N/A |
General Scenarios |
SmartP |
2*PicSize |
N/A |
Monitoring Scenarios |
The calculation method for the size of each variable block (VB) in the encoded frame memory (reference frame and reconstructed frame) is as follows:
H.264
PicSize= FrameBufSize
H.265
PicSize= FrameBufSize + mvColSize + fbcYTblSize + fbcCTblSize + subSampledSize
Please refer to the chapter “video coding” in the document 《cv180x media software development reference》for the calculation of each sub item of frame memory size
CV180x |
||
H.264 |
H.265 |
|
NormalP |
Yes |
Yes |
SmartP |
Yes |
Yes |