6.6. 模型推理
C接口详细介绍请阅读《 BMRUNTIME开发参考手册 》。
Python接口详细介绍请阅读《 sophon-sail使用手册 》。
BMRuntime用于读取BMCompiler的编译输出(.bmodel),驱动其在Sophon TPU芯片中执行。BMRuntime向用户提供了丰富的接口,便于用户移植算法,其软件架构如下:
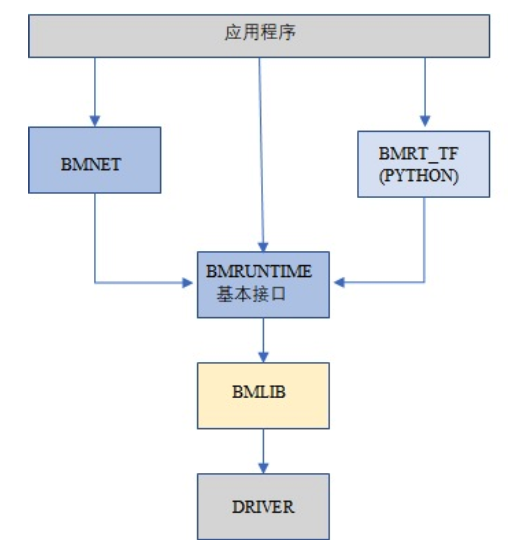
BMRuntime实现了C/C++接口,SAIL模块基于对BMRuntime和BMLib的封装实现了Python接口。本章主要介绍C和Python常用接口,主要内容如下:
BMLib 接口:负责设备Handle的管理、内存管理、数据搬运、API的发送和同步、A53使能、设置TPU工作频率等
BMRuntime的C语言接口
BMLib和BMRuntime的Python接口介绍
6.6.1. BMLib模块C接口介绍
BMLIB接口
用于设备管理,不属于BMRuntime,但需要配合使用,所以先介绍。
BMLIB接口是C语言接口,对应的头文件是bmlib_runtime.h,对应的lib库为libbmlib.so。
BMLIB接口用于设备管理,包括设备内存的管理。
BMLIB的接口很多,这里介绍应用程序通常需要用到的接口。
bm_dev_request
用于请求一个设备,得到设备句柄handle。其他设备接口,都需要指定这个设备句柄。 其中devid表示设备号,在PCIE模式下,存在多个设备时可以用于选择对应的设备;在SoC模式下,请指定为0。
1/**
2 * @name bm_dev_request
3 * @brief To create a handle for the given device
4 * @ingroup bmlib_runtime
5 *
6 * @param [out] handle The created handle
7 * @param [in] devid Specify on which device to create handle
8 * @retval BM_SUCCESS Succeeds.
9 * Other code Fails.
10 */
11bm_status_t bm_dev_request(bm_handle_t *handle, int devid);
bm_dev_free
用于释放一个设备。通常应用程序开始需要请求一个设备,退出前释放这个设备。
1/**
2 * @name bm_dev_free
3 * @brief To free a handle
4 * @param [in] handle The handle to free
5 */
6void bm_dev_free(bm_handle_t handle);
6.6.2. BMRuntime模块C接口介绍
对应的头文件为bmruntime_interface.h,对应的lib库为libbmrt.so。
用户程序使用C接口时建议使用该接口,该接口支持多种shape的静态编译网络,支持动态编译网络。
bmrt_create
1/**
2 * @name bmrt_create
3 * @brief To create the bmruntime with bm_handle.
4 * This API creates the bmruntime. It returns a void* pointer which is the pointer
5 * of bmruntime. Device id is set when get bm_handle;
6 * @param [in] bm_handle bm handle. It must be initialized by using bmlib.
7 * @retval void* the pointer of bmruntime
8 */
9void* bmrt_create(bm_handle_t bm_handle);
bmrt_destroy
1/**
2 * @name bmrt_destroy
3 * @brief To destroy the bmruntime pointer
4 * @ingroup bmruntime
5 * This API destroy the bmruntime.
6 * @param [in] p_bmrt Bmruntime that had been created
7 */
8void bmrt_destroy(void* p_bmrt);
bmrt_load_bmodel
加载bmodel文件,加载后bmruntime中就会存在若干网络的数据,后续可以对网络进行推理。
1/**
2 * @name bmrt_load_bmodel
3 * @brief To load the bmodel which is created by BM compiler
4 * This API is to load bmodel created by BM compiler.
5 * After loading bmodel, we can run the inference of neuron network.
6 * @param [in] p_bmrt Bmruntime that had been created
7 * @param [in] bmodel_path Bmodel file directory.
8 * @retval true Load context sucess.
9 * @retval false Load context failed.
10 */
11bool bmrt_load_bmodel(void* p_bmrt, const char *bmodel_path);
bmrt_load_bmodel_data
加载bmodel,不同于bmrt_load_bmodel,它的bmodel数据存在内存中
1/*
2Parameters: [in] p_bmrt - Bmruntime that had been created.
3 [in] bmodel_data - Bmodel data pointer to buffer.
4 [in] size - Bmodel data size.
5Returns: bool - true: success; false: failed.
6*/
7bool bmrt_load_bmodel_data(void* p_bmrt, const void * bmodel_data, size_t size);
bmrt_get_network_info
bmrt_get_network_info根据网络名,得到某个网络的信息
1/* bm_stage_info_t holds input shapes and output shapes;
2every network can contain one or more stages */
3typedef struct {
4bm_shape_t* input_shapes; /* input_shapes[0] / [1] / ... / [input_num-1] */
5bm_shape_t* output_shapes; /* output_shapes[0] / [1] / ... / [output_num-1] */
6} bm_stage_info_t;
7
8/* bm_tensor_info_t holds all information of one net */
9typedef struct {
10const char* name; /* net name */
11bool is_dynamic; /* dynamic or static */
12int input_num; /* number of inputs */
13char const** input_names; /* input_names[0] / [1] / .../ [input_num-1] */
14bm_data_type_t* input_dtypes; /* input_dtypes[0] / [1] / .../ [input_num-1] */
15float* input_scales; /* input_scales[0] / [1] / .../ [input_num-1] */
16int output_num; /* number of outputs */
17char const** output_names; /* output_names[0] / [1] / .../ [output_num-1] */
18bm_data_type_t* output_dtypes; /* output_dtypes[0] / [1] / .../ [output_num-1] */
19float* output_scales; /* output_scales[0] / [1] / .../ [output_num-1] */
20int stage_num; /* number of stages */
21bm_stage_info_t* stages; /* stages[0] / [1] / ... / [stage_num-1] */
22} bm_net_info_t;
bm_net_info_t表示一个网络的全部信息,bm_stage_info_t表示该网络支持的不同的shape情况。
1/**
2 * @name bmrt_get_network_info
3 * @brief To get network info by net name
4 * @param [in] p_bmrt Bmruntime that had been created
5 * @param [in] net_name Network name
6 * @retval bm_net_info_t* Pointer to net info, needn't free by user; if net name not found, will return NULL.
7 */
8const bm_net_info_t* bmrt_get_network_info(void* p_bmrt, const char* net_name);
示例代码:
1const char *model_name = "VGG_VOC0712_SSD_300X300_deploy"
2const char **net_names = NULL;
3bm_handle_t bm_handle;
4bm_dev_request(&bm_handle, 0);
5void * p_bmrt = bmrt_create(bm_handle);
6bool ret = bmrt_load_bmodel(p_bmrt, bmodel.c_str());
7std::string bmodel; //bmodel file
8int net_num = bmrt_get_network_number(p_bmrt, model_name);
9bmrt_get_network_names(p_bmrt, &net_names);
10for (int i=0; i<net_num; i++) {
11//do somthing here
12......
13}
14free(net_names);
15bmrt_destroy(p_bmrt);
16bm_dev_free(bm_handle);
bmrt_shape_count
接口声明如下:
1/*
2number of shape elements, shape should not be NULL and num_dims should not large than BM_MAX_DIMS_NUM
3*/
4uint64_t bmrt_shape_count(const bm_shape_t* shape);
可以得到shape的元素个数。
比如num_dims为4,则得到的个数为dims[0]*dims[1]*dims[2]*dims[3]
bm_shape_t 结构介绍:
1typedef struct {
2int num_dims;
3int dims[BM_MAX_DIMS_NUM];
4} bm_shape_t;
bm_shape_t表示tensor的shape,目前最大支持8维的tensor。其中num_dims为tensor的实际维度数,dims为各维度值,dims的各维度值从[0]开始,比如(n, c, h, w)四维分别对应(dims[0], dims[1], dims[2], dims[3])。
如果是常量shape,初始化参考如下:
1bm_shape_t shape = {4, {4,3,228,228}};
2bm_shape_t shape_array[2] = {
3{4, {4,3,28,28}}, // [0]
4{2, {2,4}}, // [1]
5}
bm_image_from_mat
1//if use this function you need to open USE_OPENCV macro in include/bmruntime/bm_wrapper.hpp
2/**
3* @name bm_image_from_mat
4* @brief Convert opencv Mat object to BMCV bm_image object
5* @param [in] in OPENCV mat object
6* @param [out] out BMCV bm_image object
7* @retval true Launch success.
8* @retval false Launch failed.
9*/
10static inline bool bm_image_from_mat (cv::Mat &in, bm_image &out)
1//* @brief Convert opencv multi Mat object to multi BMCV bm_image object
2static inline bool bm_image_from_mat (std::vector<cv::Mat> &in, std::vector<bm_image> &out)
bm_image_from_frame
1/**
2 * @name bm_image_from_frame
3 * @brief Convert ffmpeg a avframe object to a BMCV bm_image object
4 * @ingroup bmruntime
5 *
6 * @param [in] bm_handle the low level device handle
7 * @param [in] in a read-only avframe
8 * @param [out] out an uninitialized BMCV bm_image object
9 use bm_image_destroy function to free out parameter until you no longer useing it.
10 * @retval true change success.
11 * @retval false change failed.
12 */
13
14static inline bool bm_image_from_frame (bm_handle_t &bm_handle,
15 AVFrame &in,
16 bm_image &out)
1/**
2 * @name bm_image_from_frame
3 * @brief Convert ffmpeg avframe to BMCV bm_image object
4 * @ingroup bmruntime
5 *
6 * @param [in] bm_handle the low level device handle
7 * @param [in] in a read-only ffmpeg avframe vector
8 * @param [out] out an uninitialized BMCV bm_image vector
9 use bm_image_destroy function to free out parameter until you no longer useing it.
10 * @retval true change success.
11 * @retval false chaneg failed.
12 */
13static inline bool bm_image_from_frame (bm_handle_t &bm_handle,
14 std::vector<AVFrame> &in,
15 std::vector<bm_image> &out)
bm_inference
1//if use this function you need to open USE_OPENCV macro in include/bmruntime/bm_wrapper.hpp
2/**
3* @name bm_inference
4* @brief A block inference wrapper call
5* @ingroup bmruntime
6*
7* This API supports the neuron nework that is static-compiled or dynamic-compiled
8* After calling this API, inference on TPU is launched. And the CPU
9* program will be blocked.
10* This API support single input && single output, and multi thread safety
11*
12* @param [in] p_bmrt Bmruntime that had been created
13* @param [in] input bm_image of single-input data
14* @param [in] output Pointer of single-output buffer
15* @param [in] net_name The name of the neuron network
16* @param [in] input_shape single-input shape
17*
18* @retval true Launch success.
19* @retval false Launch failed.
20*/
21static inline bool bm_inference (void *p_bmrt,
22 bm_image *input,
23 void *output,
24 bm_shape_t input_shape,
25 const char *net_name)
1// * This API support single input && multi output, and multi thread safety
2static inline bool bm_inference (void *p_bmrt,
3 bm_image *input,
4 std::vector<void*> outputs,
5 bm_shape_t input_shape,
6 const char *net_name)
1// * This API support multiple inputs && multiple outputs, and multi thread safety
2static inline bool bm_inference (void *p_bmrt,
3 std::vector<bm_image*> inputs,
4 std::vector<void*> outputs,
5 std::vector<bm_shape_t> input_shapes,
6 const char *net_name)
6.6.3. Python接口
本章节只简要介绍了 YOLOv5 用例中所用的接口函数。
更多接口定义请查阅《 sophon-sail使用手册 》。
Engine
1def __init__(tpu_id):
2""" Constructor does not load bmodel.
3Parameters
4---------
5tpu_id : int TPU ID. You can use bm-smi to see available IDs
6"""
load
1def load(bmodel_path):
2"""Load bmodel from file.
3Parameters
4---------
5bmodel_path : str Path to bmode
6"""
set_io_mode
1def set_io_mode(mode):
2""" Set IOMode for a graph.
3Parameters
4---------
5mode : sail.IOMode Specified io mode
6"""
get_graph_names
1def get_graph_names():
2""" Get all graph names in the loaded bmodels.
3Returns
4------
5graph_names : list Graph names list in loaded context
6"""
get_input_names
1def get_input_names(graph_name):
2""" Get all input tensor names of the specified graph.
3Parameters
4---------
5graph_name : str Specified graph name
6Returns
7------
8input_names : list All the input tensor names of the graph
9"""
get_output_names
1def get_output_names(graph_name):
2""" Get all output tensor names of the specified graph.
3Parameters
4---------
5graph_name : str Specified graph name
6Returns
7------
8input_names : list All the output tensor names of the graph
9"""
sail.IOMode
1# Input tensors are in system memory while output tensors are in device memory sail.IOMode.SYSI
2# Input tensors are in device memory while output tensors are in system memory.
3sail.IOMode.SYSO
4# Both input and output tensors are in system memory.
5sail.IOMode.SYSIO
6# Both input and output tensors are in device memory.
7ail.IOMode.DEVIO
sail.Tensor
1def __init__(handle, shape, dtype, own_sys_data, own_dev_data):
2""" Constructor allocates system memory and device memory of the tensor.
3Parameters
4---------
5handle : sail.Handle Handle instance
6shape : tuple Tensor shape
7dytpe : sail.Dtype Data type
8own_sys_data : bool Indicator of whether own system memory
9own_dev_data : bool Indicator of whether own device memory
10"""
get_input_dtype
1def get_input_dtype(graph_name, tensor_name):
2""" Get scale of an input tensor. Only used for int8 models.
3Parameters
4---------
5graph_name : str The specified graph name tensor_name : str The specified output tensor name
6Returns
7------
8scale: sail.Dtype Data type of the input tensor
9"""
get_output_dtype
1def get_output_dtype(graph_name, tensor_name):
2""" Get the shape of an output tensor in a graph.
3Parameters
4---------
5graph_name : str The specified graph name tensor_name : str The specified output tensor name
6Returns
7------
8tensor_shape : list The shape of the tensor
9"""
process
1def process(graph_name, input_tensors, output_tensors):
2""" Inference with provided input and output tensors.
3Parameters
4---------
5graph_name : str The specified graph name
6input_tensors : dict {str : sail.Tensor} Input tensors managed by user
7output_tensors : dict {str : sail.Tensor} Output tensors managed by user
8"""
get_input_scale
1def get_input_scale(graph_name, tensor_name):
2""" Get scale of an input tensor. Only used for int8 models.
3Parameters
4---------
5graph_name : str The specified graph name tensor_name : str The specified output tensor name
6Returns
7------
8scale: float32 Scale of the input tensor
9"""
get_output_scale
1def get_output_scale(graph_name, tensor_name)
2""" Get scale of an output tensor. Only used for int8 models.
3
4Parameters
5----------
6graph_name : str
7 The specified graph name
8tensor_name : str
9 The specified output tensor name
10
11Returns
12-------
13scale: float32
14 Scale of the output tensor
15"""
get_input_shape
1def get_input_shape(graph_name, tensor_name):
2""" Get the maximum dimension shape of an input tensor in a graph.
3 There are cases that there are multiple input shapes in one input name,
4 This API only returns the maximum dimension one for the memory allocation
5 in order to get the best performance.
6
7Parameters
8----------
9graph_name : str
10 The specified graph name
11tensor_name : str
12 The specified input tensor name
13
14Returns
15-------
16tensor_shape : list
17 The maxmim dimension shape of the tensor
18"""
get_output_shape
1def get_output_shape(graph_name, tensor_name):
2""" Get the shape of an output tensor in a graph.
3
4Parameters
5----------
6graph_name : str
7 The specified graph name
8tensor_name : str
9 The specified output tensor name
10
11Returns
12-------
13tensor_shape : list
14 The shape of the tensor
15"""